ABOUT- SWISS BLUE TOPAZ
Topaz, a readily available and generally inexpensive gemstone, is used in many varieties of jewelry and forms in an assortment of colors
History and Origins
Topaz’s history dates back at least two thousand years ago to ancient Egyptian times. For theses ancient Egyptians, it was commonly believed that yellow topaz was given its golden color from the Sun God called Ra.
The term “topaz” is believed to be a Middle English word, which was attained from the Old French word "Topace" and "Topazus" in Latin. The root of both is in the Greek word "Topazios" or "Topazion,” the ancient name of an island in The Red Sea where ancient Greeks mined a yellow gem thought to be topaz. The word "topaz" could also have originated from the term “tapas”, which is a word in – the ancient language of India – meaning "fire."
Topaz is mentioned in the Christian Old Testament, but may have been mistaken for chrysolite instead. Ancient Romans believed that yellow topaz could help keep them from being poisoned, while ancient Greeks believed that it bestowed strength upon its owner.
During the Renaissance era in Europe, many thought that topaz could annul magic spells and dissipate anger. For centuries, people in India believed that it would assure a long life, beauty and intelligence in its wearer.
The name for imperial topaz originated in nineteenth-century Russia. At the time, the Ural Mountains were topaz’s leading source, and the pink gemstone mined there was named to honor the Russian czar. Ownership of the gem was restricted to the royal family.
Formation and Physical Properties
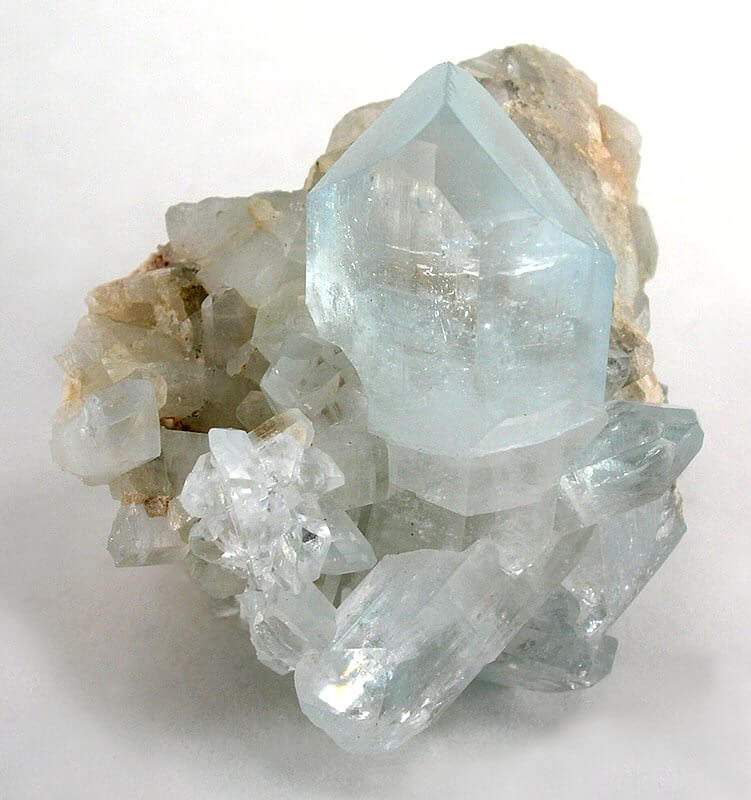

Topaz rough. Rob Lavinsky, iRocks.com – CC-BY-SA-3.0
Topaz is a silicate mineral belonging to the aluminum and fluorine family and has a formula of Al2SiO4(F,OH)2. It has rating of 8 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness and can form in a variety of colors. Its crystal system is orthorhombic, with a crystal habit that are prismatic, columnar, compact or massive.
Topaz’s faults include principally impure color, fissures in the direction of cleavage, and turbidity. Another fault is that there are also cavities that form, either vacuous or filled with liquids. Most topaz crystallizes in granitic pegmatites or in vapor cavities in rhyolite lava flows.
Localities
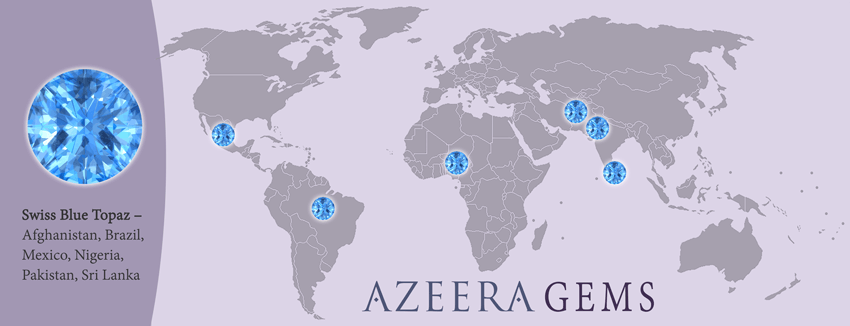
Currently, the largest producer of topaz is Brazil. Other major localities that source rubies include:
- Afghanistan
- Australia
- Brazil
- Czech Republic
- Flinders Island
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- Mexico
- Nigeria
- Normway
- Pakistan
- Russia
- Sri Lanka
- Sweden
- United States of America – Utah
Certain clear topaz from Brazil can form in crystals the size of boulders and can weigh hundreds of pounds – many of these are currently in museum collections around the world. The Topaz of Aurangzeb, observed by Jean Baptiste Tavernier was measured at 157.75 carats, and the American Golden Topaz, a more recently discovered stone, was measured at a colossal 22,892.50 carats.